Bootstrap Azure Subscription for DevOps
Consider a large food manufacturer that produces beef products on a global scale. Currently the manufacturer works with a large number of systems, processes and integration patterns, causing issues. What if we could simplify this process with a single real-time pipeline. Enter, stream the dream!
A typical process of a food manufacturer is depicted below:
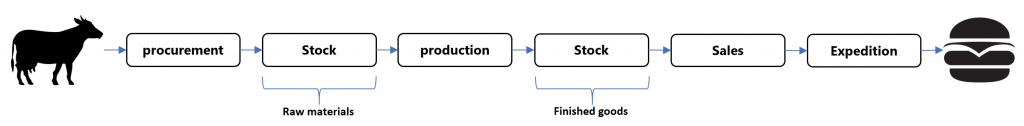
Most companies allocate specific systems and functionalities for each step in this process to store information effectively. In the schematic overview below, a MES system is directly connected to the machines. They log each production step together with its processing- and machine-data.
An ERP system is used for administrative tasks and contains processing planning-, sales-, and inventory data. Combining data from these systems (and other in- or external data sources) into a BI system leads to a batch-driven solution. It provides business with valuable actionable insights on a daily basis. A schematic overview of this typical dataflow is represented in the figure below.
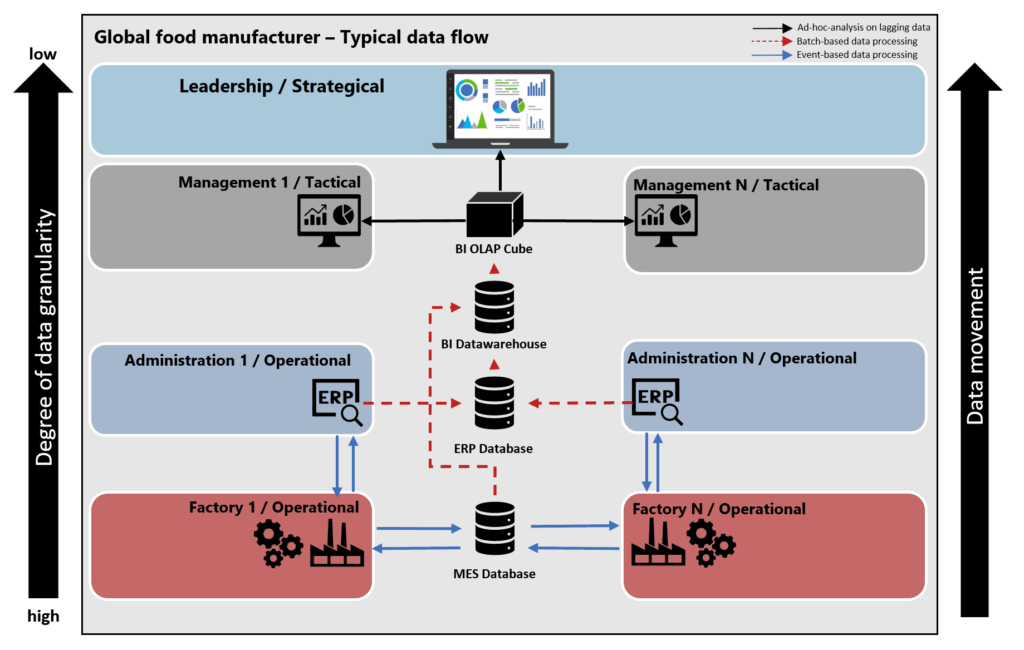
Having numerous information systems, each having a specific purpose and dealing with their respective granularity, timeliness, and data formats, leads to a variety of integration patterns (i.e. file-based, ETL, batch- and event-based-patterns). This results in unwanted complexity and dependencies in an organization’s dataflow. Above all, does it answer all the users’ questions at all organizational levels?
Instant action on production or health-safety issues in food production is of utmost importance for effective control and response. Having only a daily overview of the day before will not help a team lead to act in an instant when a production or health-safety issue arises.
A team lead should be able to act directly whilst management should be informed to adapt strategy in the shortest amount of time possible. Hence, an Enterprise Streaming Platform (ESP) is the solution!
An ESP enables a food manufacturer to have (near) real-time insights and availability of all data within the organization. ESP considers everything to be an “event”. This can be a goods receiving, inventory movement, production registration, invoicing, or financial posting.
An ESP differs from an Eventbus-platform by persisting events and making them available in a "topic" for every information system. Looking at an Eventbus-platform, it puts events on a queue and waits until an information system consumes it. Subsequently it deletes the event from the queue.
An ESP persisting events allows other systems to consume events in the exact order as the preceding information system. Thereby, providing each information system with an identical set of data and dataflow. This gives the ESP a significant advantage compared to an Eventbus-platform.
Plotting an ESP on the food manufacturer layout we can observe the following schematic overview:
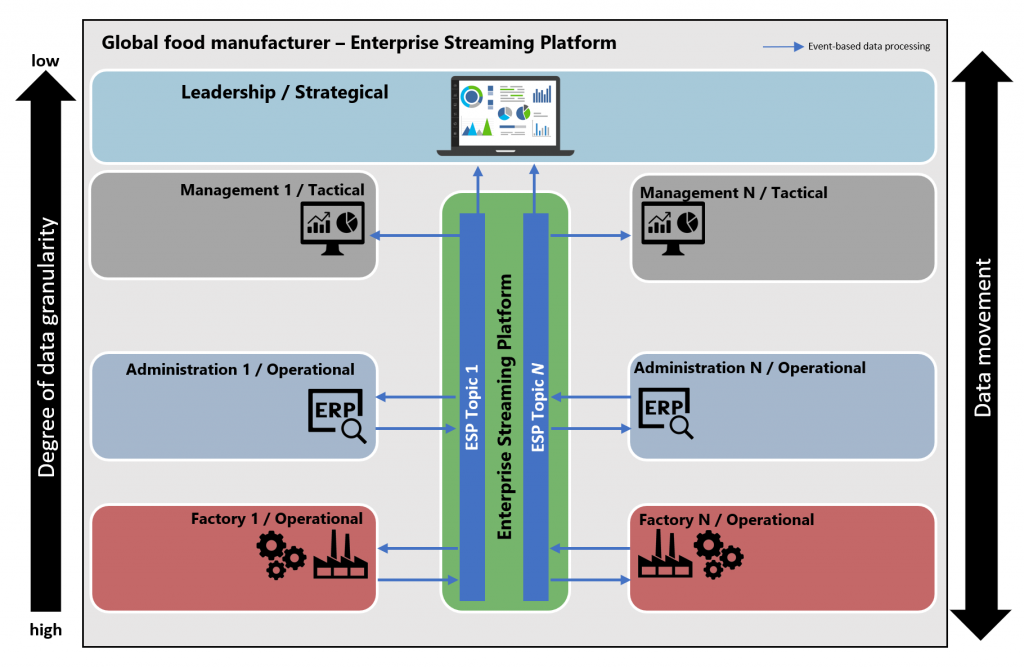
Comparing layouts, switching to a single ESP reduced the data platform's complexity, streamlining integration to one pattern in food manufacturing. As a result, we moved from a batch-driven environment to an event-based-environment across all levels of the organization.
Secondly, we have made all data readily and rapidly available to any information system or team that wants to consume or produce data. This will enable a food manufacturer to become truly data-driven, resulting in a competitive advantage. In addition, an ESP provides teams with the opportunity to create innovative solutions and the ability to apply data science or machine learning techniques on real-time data, leading to new actionable insights, process optimizations, and potentially increased margins.
When using an ESP it becomes extremely easy to integrate various existing and new information systems through a single integration pattern and platform. Leveraging the ESP-capabilities simplifies things drastically as there are no more custom point-2-point-application-integration patterns required (e.g., SAP with Exact Online; CSB-System with external MES, etc.).
Enabling everyone via a single (near)-real-time ESP transforms how we work and think about data, unlocking its untapped potential. At Food For Analytics, we believe in the value of an ESP—a Scalable, Flexible, and Robust real-time data platform. We see it as a must to become data-driven and move towards industry 4.0.
Interested? Reach out to us directly!
The implementation of an ESP addresses specific challenges in global food manufacturing by simplifying data integration and processing. It solves the granularity-issue by treating every event, such as goods receiving or production registration, as an individual data point. Regardless of the system it originates from.
This uniform approach ensures consistency and eliminates the need for complex mappings between different data formats and levels of detail. Additionally, ESPs facilitate real-time data processing, enabling organizations to respond swiftly to production or health-safety issues.
Benefits include increased operational efficiency, improved decision-making, and the ability to leverage through real-time insights for process optimization.
By moving from batch-driven solutions to event-based environments, companies can streamline their data infrastructure and unlock new opportunities for innovation.
Challenges could include system compatibility and integration with existing infrastructure. Secondly, organizational barriers such as resistance to change and the need for cultural shift towards data-driven decision-making.
Additionally, data security and compliance with legislation across different countries may pose complexities that need to be addressed as well.